Products Details

D-Ribose 50-69-1 manufacturer
D-Ribose 50-69-1 in stock
D-Ribose 50-69-1 price
Melting point:88-92 ° C
Specific rotation - 20.8 ° (C = 4, H2O)
It can be used as pharmaceutical raw materials, health products, intermediates, food additives, etc
Synonyms:RIBOSE, D-(-)-;d-ribos;D-RIB;D(-)-Ribose,99+%;R-RIBOSE;RIBONIC ACID-Gamma-LACTONE, D-(+)-(RG);Ribose (300 mg);D-Ribose/D(-)-Ribose
CAS:50-69-1
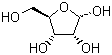
MF:C5H10O5
MW:150.13
EINECS:200-059-4
Product Categories:Sugars, Carbohydrates & Glucosides;FINE Chemical & INTERMEDIATES;Basic Sugars (Mono & Oligosaccharides);Biochemistry;Nucleosides, Nucleotides & Related Reagents;Ribose;Riboses and 2'-Deoxyriboses;Sugars;Nutritional Supplements;Nutritional fortification substances;Carbohydrates & Derivatives;Co-factor/nucleoside;Alphabetical Listings;Flavors and Fragrances;Q-Z;Biochemicals Found in Plants;MonosaccharidesBiochemicals Found in Plants;Simple sugars;Carbohydrate Synthesis;Carbohydrates;Specialty Synthesis;Carbohydrate LibraryBiochemicals Found in Plants;CarbohydrateMetabolomics;Metabolic Libraries;Metabolic Pathways;Metabolites and Cofactors on the Metabolic Pathways Chart
D-Ribose Chemical Properties
Melting point 88-92 °C(lit.)
alpha -20.8 o (c=4, H2O)
Boiling point 191.65°C (rough estimate)
density 1.1897 (rough estimate)
FEMA 3793 | D-RIBOSE
refractive index:-21 ° (C=1, H2O)
storage temp. 2-8°C
solubility H2O: 0.1 g/mL, clear, colorless to light yellow
pKa12.46±0.20(Predicted)
form Crystalline Powder
color White to light beige or slightly yellow
PH Range7
optical activity[α]21/D 19.7°, c = 4 in H2O
Water Solubility Soluble in water. Insoluble in ether.
Sensitive Hygroscopic
Merck 14,8204
BRN:1723081
InChIKey:HMFHBZSHGGEWLO-SOOFDHNKSA-N
CAS DataBase Reference:50-69-1(CAS DataBase Reference)
NIST Chemistry Reference:D-Ribose(50-69-1)
EPA Substance Registry System:D-Ribose (50-69-1)
Safety Information
Hazard Codes Xi
Risk Statements 36/38
Safety Statements 24/25-37/39-26
WGK Germany 3
RTECS VJ2275000
F 3-10
TSCA Yes
HS Code 29400090
D-Ribose Usage And Synthesis
Description:For pharmaceutical raw materials, health products, intermediates, food additives and so on
Ribose-5-phosphate, supports biosynthesis of tryptophan and histidine, and is one of the components of the phosphate pentose synthesis pathway.
Chemical Properties:White powder
Chemical Properties:D-Ribose is a carbohydrate, or sugar, used by all living cells and is an essential component in living organisms for energy production. It has a sweet taste.
OccurrenceReported found in boiled crab, hen egg, catfish, whitefish, haddock, stored beef, stored veal, milk, applesauce, potato, rapeseed, roasted coffee, fresh coffee and shrimp.
Uses:It is produced by microorganism fermentation of glucose in a fermentation culture medium without adding calcium carbonate.
Uses:D-Ribose is produced by microorganism fermentation of glucose in a fermentation culture medium without adding calcium carbonate.
Definition:ChEBI: A ribofuranose having D-configuration.
Preparation:By fermentation technology.
Biological Activity:D-ribose is a natural sugar that our bodies produce for a variety of purposes most notably encrgy in the form of ATP(adenosine triphosphate), which powers every cell in our body. Ribose is crucial for the synthesis of energy (ATP) and without it, your cells run out of energy and the health of the cell is compromised. Supplementing with ribose improves cell function by restoring energy.
One of the most vital organs to suffer energy depletion is the heart. That is why so much of the research on D-ribose has focused on the impact of supplement ribose in heart disease. Although ribose is classified as a sugar, when taken orally, it does not have any impact on blood sugar like glucose. Instead, it is used for energy production and energy recovery. Every cell in the body has the capacity to make ribose. But more ribose may be needed than the cell can produce when cells are metabolically stressed, such as with strenuous exercise or disease. When the cells are metabolically stressed they tend to consume more glucose rather than producing more ribose. This can dramatically affect recovery.
Purification Methods:Crystallise -D(-)-ribose from aqueous 80% EtOH, dry it under vacuum at 60o over P2O5 and store it in a vacuum desiccator. It exhibits a complex mutarotation with : [] D 10 -23.1o (1.5minutes), -21.3o (5minutes), -19.5o (10minutes), -19.1o (30minutes), -21.2o (60minutes), -23.1o (120minutes), -23.7o (300minutes), (c 4.5, H2O) [Phelps et al. J Am Chem Soc 56 748 1934]. 1H NMR in D2O at 44o shows 17% -pyranose, 59% -pyranose, 9% -furanose and 15% -furanose forms with furanose -H at 5.34ppm (J 3.0Hz) and -H at 5.31 (J 1.7Hz) [Angyal Adv Carbohydr Chem 42 15 1984, Angyal & Pickles Aust J Chem 25 1711 1972]. The phenylhydrazone crystallises from aqueous pyridine in yellow needles, m 163-164o, and the benzylphenylhydrazone has m 127-128o [Snowden J Am Chem Soc 72 808 1950.] [Beilstein 1 IV 4211.]
Displaying 1 to 3 (of 6 products)